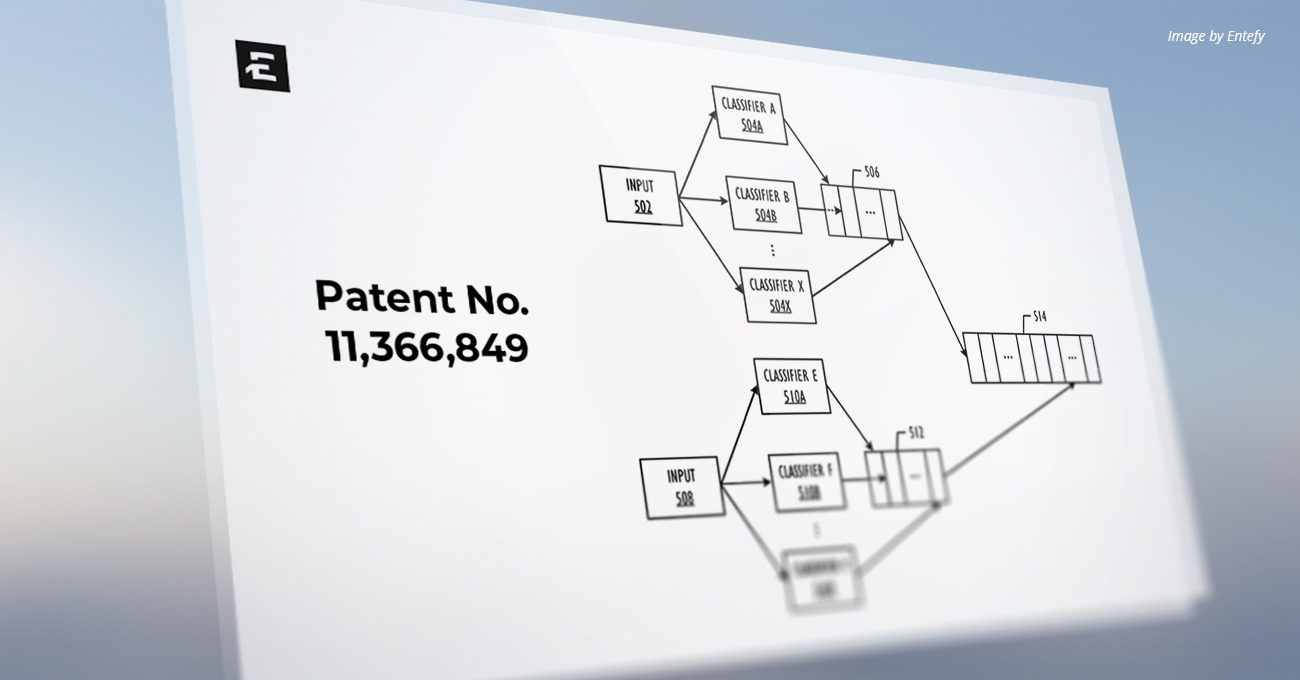
U.S. Patent Number: 11,366,849
Patent Title: System and method for unifying feature vectors in a knowledge graph
Issue Date: June 21, 2022
Inventors: Ghafourifar, et al.
Assignee: Entefy Inc.
Patent Abstract
Disclosed are apparatuses, methods, and computer readable media for improved multi-datatype searching comprising receiving a search query of a first datatype, generating a vector of the first datatype describing the search query, expanding the vector of the first datatype to include a second datatype vector, wherein the second datatype vector is different from the first datatype but may be conceptually equivalent, and wherein the second datatype is associated with the vector of the first datatype, and performing a search based on the first datatype and a search on the second datatype.
USPTO Technical Field
This disclosure relates generally to apparatuses, methods, and computer readable media for a unified knowledge vector for improved multi-format search.
Background
Machine learning and pattern recognition software system can be harnessed to perform various artificial intelligence tasks or services, such as object recognition, translation, and autonomous driving. These tasks or services may be based on a number of types of input, including speech, text, images, video, light detection and ranging (LIDAR), etc. Patterns may be determined to analyze and make inferences about the input. In certain cases, classifiers may be used to recognize various aspects of the input and the output of these classifiers may be organized as a vector. Vectors generally represent an item or concept as described by the classifiers. As an example, for a picture of a face, various classifiers trained to recognize specific facial features may be run to help identify a person in the picture. These classifiers may each output scores indicating how much the face matches with specific facial feature each classifier is trained to identify. These scores may be collected into a facial image vector and the facial image vector compared to a database of facial image vectors describing other face images to find a match. This comparison may be, for example, based on the output of clustering algorithms such as K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) and other forms of analysis of vectors representing attributes detected between different facial images.
These comparisons work within single data type, but break down across different types of data since a vector describing a concept associated with a first data type may not accurately describe that same concept in a second data type. Additionally, the first data concept vector may represent relationship X with various other concept vectors in the first data space, whereas that same concept vector may not exist or may represent a different relationship Y with other concepts in the second data space. For an example, a vector representing an image of an intersection of two roads may be more closely related, for example as a part of a KNN analysis, to a curved road rather than two lines or objects intersecting each other. However, in text, a vector for an intersection may be more closely related to a crossing point or line than anything related to roads. Moreover, for the image data type, the physical location or angle of the image may influence the resulting vector describing the image. This in turn may influence the KNN analysis. For example, a particular image of an intersection may be partially occluded by a traffic sign for the intersection, which may result in the vector being more closely related to a merge traffic sign. Attempting to map this vector across data types into text may then point to a completely different concept than expected.
The subject matter of the present disclosure is directed to overcoming, or at least reducing the effects of, one or more of the problems set forth above. To address these and other issues, techniques for improved cross data search by enabling comparisons of feature vectors across data types are described herein.
Read the full patent here.
ABOUT ENTEFY
Entefy is an enterprise AI software company. Entefy’s patented, multisensory AI technology delivers on the promise of the intelligent enterprise, at unprecedented speed and scale.
Entefy products and services help organizations transform their legacy systems and business processes—everything from knowledge management to workflows, supply chain logistics, cybersecurity, data privacy, customer engagement, quality assurance, forecasting, and more. Entefy’s customers vary in size from SMEs to large global public companies across multiple industries including financial services, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
To leap ahead and future proof your business with Entefy’s breakthrough AI technologies, visit www.entefy.com or contact us at contact@entefy.com.