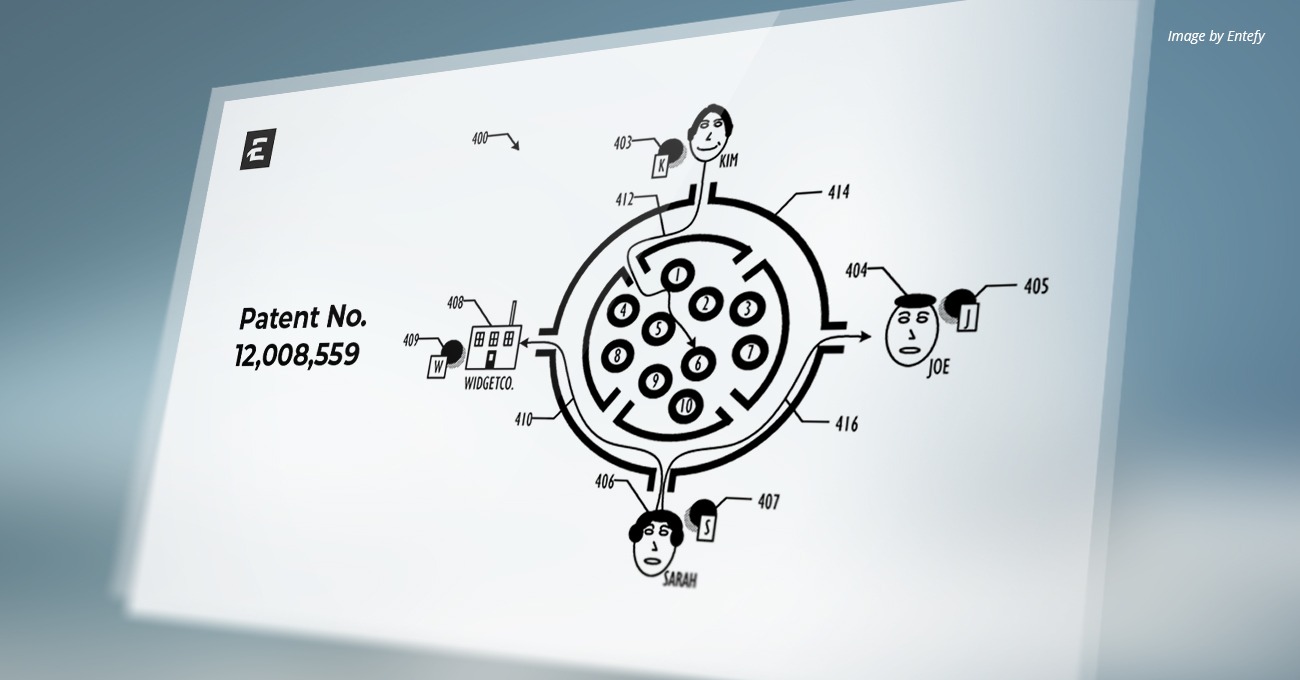
U.S. Patent Number: 12,008,559
Patent Title: Decentralized blockchain for artificial intelligence-enabled multi-party skills exchanges over a network
Issue Date: June 11, 2024
Inventors: Ghafourifar, et al.
Assignee: Entefy Inc.
Patent Abstract
An improved decentralized, blockchain-driven network for artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled skills exchange between Intelligent Personal Assistants (IPAs) in a network is disclosed that is configured to perform computational tasks or services (also referred to herein as “skills”) in an optimally-efficient fashion. In some embodiments, this may comprise a first IPA paying an agreed cost to a second IPA to perform a particular skill in a more optimally-efficient fashion. In some embodiments, a skills registry is published, comprising benchmark analyses and costs for the skills offered by the various nodes on the skills exchange network. In other embodiments, a transaction ledger is maintained that provides a record of all transactions performed across the network in a tamper-proof and auditable fashion, e.g., via the use of blockchain technology. Over time, the AI-enabled nodes in the system may learn to scale, replicate, and transact with each other in an optimized—and fully autonomous—fashion.
USPTO Technical Field
This disclosure relates generally to apparatuses, methods, and computer readable media for a decentralized, secure network for artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled performance and exchange of computational tasks and services between network nodes.
Background
Intelligent personal assistant (IPA) software systems comprise software agents that can perform various functions, e.g., computational tasks or services, on behalf of an individual user or users. IPAs, as used herein, may simply be thought of as computational “containers” for certain functionalities. The functionalities that are able to be performed by a given IPA at a particular moment in time may be based on a number of factors, including: a user’s geolocation, a user’s preferences, an ability to access information from a variety of online sources, the processing power and/or current performance load of a physical instance that the IPA is currently being executed on, and the historical training/modification/customization that has been performed on the IPA. As such, current IPA software systems have fundamental limitations in terms of their capabilities and abilities to perform certain computational tasks.
For example, in some instances, a first IPA executing on a first device on a network may be able to perform a particular first computational task or service (also referred to herein as a “skill”) with a very high degree of accuracy, but may be executing on a physical instance that lacks the necessary computational power or capacity to perform the particular first computational task or service in a reasonable amount of time. Likewise, a second IPA, e.g., being executed on a device belonging to another user on the same network, may have excellent computational power and capacity, but not have been trained to perform the first computational task or service with a high degree of accuracy. As such, the particular first computational task or service is not likely to be able to be efficiently performed by either the first IPA or the second IPA, causing, in effect, an inevitable marketplace inefficiency in the overall skills network.
Such a scenario may not provide for a satisfactory (or efficient) user experience across the many users and/or nodes of the network. In the context of AI-enabled IPAs, the IPAs may be able to “learn” and improve their performance of certain computational tasks or services over time. AI-enabled IPAs may also be able to determine, over time, more efficient usages of the network’s overall computational capacity to perform computational tasks or services at a high level of performance and at a low operational cost, e.g., by ‘farming out’ certain computational tasks to other IPAs and/or nodes in the network that can perform the task in a more optimal manner.
However, in order to be able to act, react, and interoperate in an efficient manner, the various IPAs distributed across a network must have accurate information as to the current status of the various skills that the nodes on the network are able to perform (e.g., in terms of benchmarking scores, availability, and/or costs)—as well as the ability to determine the most optimal nodes that could be used to perform such skills, given computational and cost constraints.
Moreover, in order to reliably provide “value,” i.e., payment for services rendered, to other nodes in the aforementioned network for the performance of skills in an optimized manner, it is important that a secure ledger of transactions performed across the network be maintained in a tamper-proof and auditable fashion.
The subject matter of the present disclosure is directed to overcoming, or at least reducing the effects of, one or more of the problems set forth above. To address these and other issues, techniques that enable a decentralized, secure network for the AI-enabled performance and exchange of computational tasks and services between nodes on a network are described herein.
Read the full patent here.
ABOUT ENTEFY
Entefy is an enterprise AI software company. Entefy’s patented, multisensory AI technology delivers on the promise of the intelligent enterprise, at unprecedented speed and scale.
Entefy products and services help organizations transform their legacy systems and business processes—everything from knowledge management to workflows, supply chain logistics, cybersecurity, data privacy, customer engagement, quality assurance, forecasting, and more. Entefy’s customers vary in size from SMEs to large global public companies across multiple industries including financial services, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
To leap ahead and future proof your business with Entefy’s breakthrough AI technologies, visit www.entefy.com or contact us at contact@entefy.com.